Guaranteed microbiological safety
Microbiological testing is an essential step to ensure that a product is safe, stable, and compliant with current regulations.
Before being placed on the market, every product must demonstrate that it doesn’t pose risks to human health when used under normal or reasonably foreseeable conditions.
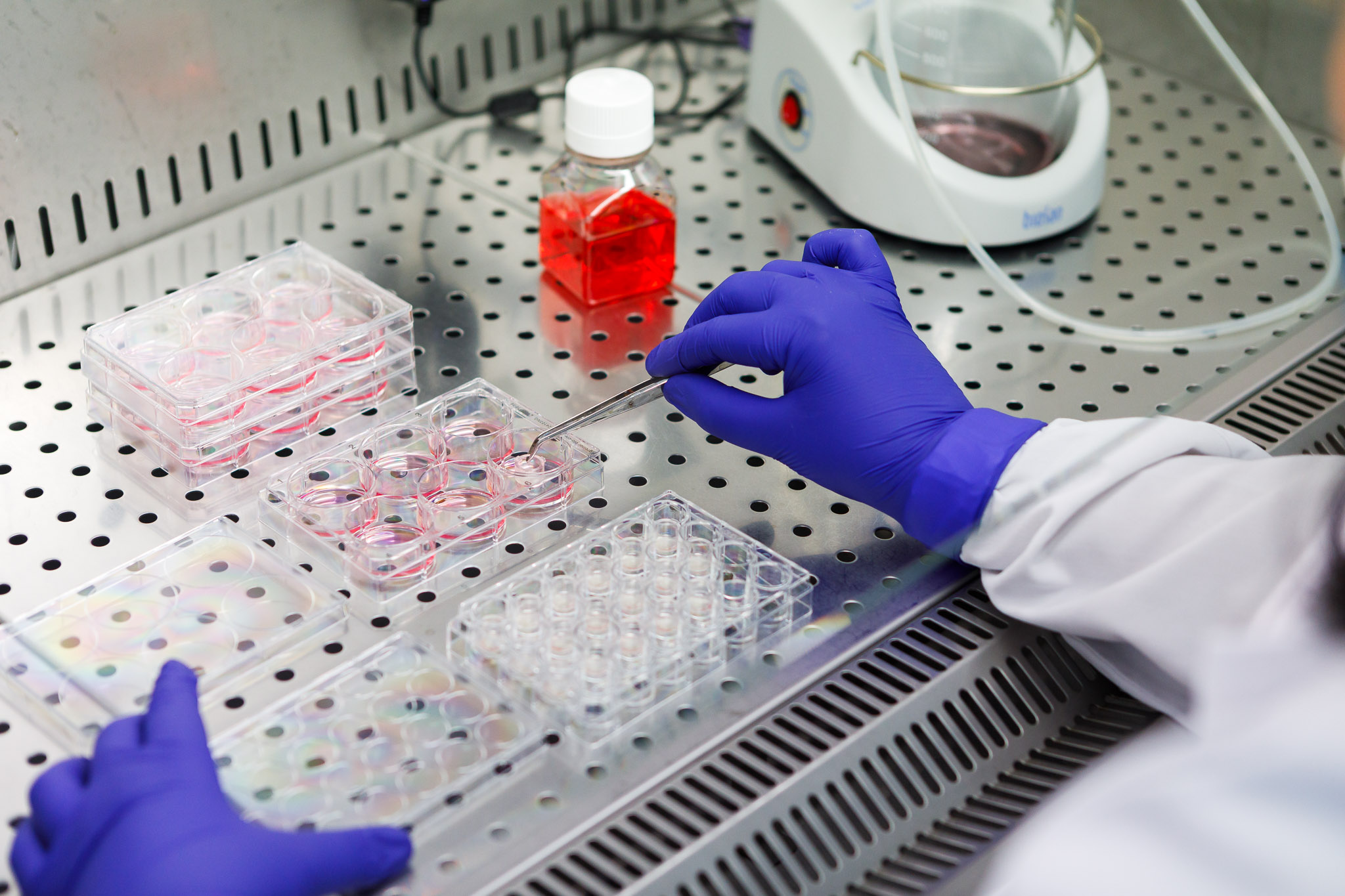

At Bio Basic Lab, and in collaboration with specialized laboratories and university institutes, we perform microbiological safety and efficacy analyses on finished products, raw materials, and packaging, following validated protocols and in full compliance with current legislative requirements.
Bio Basic also supports companies by carrying out environmental and production-process monitoring activities, ensuring quality control and preventing contamination.